
Beryllium copper is a highly versatile material that plays a critical role in the electronics and telecommunications industries. According to research, nearly half of all beryllium copper is used in these sectors for manufacturing telecommunication infrastructure, computers, and mobile phones, enabling seamless global communication. Its unique combination of high electrical conductivity, strength, and durability makes it an essential component in modern technology. Without this alloy, many of the devices we rely on daily would not function as efficiently or reliably.
Table of contents
- Applications of Beryllium Copper in Electronics
- BeCu Electrical Conductivity
- Grades of Beryllium Copper
- C17200 Beryllium Copper Heat Treatment Process
- Beryllium Copper Alloys Composition
- BeCu Mechanical Properties
- Cryogenic Temperatures Properties of Berylco 25
- Beryllium Copper Alloys Physical Properties
- Applications of Beryllium Copper in Telecommunications
C17200 Beryllium Copper is Used in Fiber Optic Cables
Beryllium copper, specifically grade C17200, is widely utilized in fiber optic cables due to its exceptional properties. One of its key advantages is its high tensile strength, which is achieved through precipitation hardening. This allows it to withstand significant bending forces without deforming, making it ideal for use in flexible and durable cable systems.
- Good Electrical Conductivity: It provides excellent electrical performance, making it suitable for high-current applications where efficiency is crucial.
- Formability: As an age-hardenable alloy, it can be easily shaped into complex forms without requiring additional heat treatment after molding or stamping.
- Fatigue Strength: Offers remarkable resistance to fatigue, ensuring long-term reliability in components subjected to repeated stress.
- Corrosion Resistance: Demonstrates strong resistance to corrosion, protecting against harsh environments and extending service life.
- Heat Resistance: Maintains mechanical integrity at elevated temperatures, allowing it to perform effectively across a wide temperature range.
Applications of Beryllium Copper in Electronics

| Electrical Components |
| Fuse Clips |
Electrical Switch / Relay Blades |
Switch Parts |
| Relay Parts |
Spring Connectors |
Connectors |
| Contact Bridges |
Current Carrying |
Belleville Washers |
| Clips |
Navigational Instruments |
 |
Beryllium Copper Alloys Offer High Strength, Hardness, and Electrical Conductivity
BeCu Electrical Conductivity
C (%IACS) = 1.7241/p20 x 100
where Ï20 (µΩ • cm) is the electrical resistivity of the alloy at 20°C.
| Berylco 14 & 8 |
| Before ageing |
After standard ageing |
Mill hardened |
| 22 to 25 % IACS |
45 to 48 % IACS |
45 to 65 % IACS* |
| Berylco 25 & 165 |
| Before ageing |
After standard ageing |
Mill hardened |
| 15 to 18 % IACS |
22 to 23 % IACS |
20 to 28 % IACS* |
Grades of Beryllium Copper
| Â |
UNS C17200 |
UNS C17510 |
UNS C17000 |
UNS C17500 |
UNS C17300 |
| Machinability rate |
20% |
– |
20% |
– |
20%. |
| Weldability |
- Coated metal arc welding
- Butt welding
- Spot welding
- Seam welding
- Gas shielded arc welding
|
- Seam welding
- Butt welding
- Gas shielded arc welding
- Brazing
|
- Brazing
- Gas shielded arc welding
- Coated metal arc welding
- Soldering
|
- Seam welding
- Butt welding
- Brazing
- Soldering
|
- Gas shielded arc welding
- Brazing
- Soldering
|
| Forging temperature |
649 to 816°C (1200 to 1500°F) |
648 and 885°C (1200 and 1625°F) |
649 to 816°C (1200 to 1500°F) |
649 and 885°C (1200 and 1625°F) |
649 to 816°C (1200 to 1500°F) |
| Hot Working |
Good |
Excellent |
Good |
Good hot forming capacity |
Good |
| Cold Working |
Excellent |
Excellent cold working capacity |
Excellent |
Excellent |
Excellent |
| Annealing |
774 to 802°C (1425 to 1475°F) |
– |
774 to 802°C (1425 to 1475°F) |
– |
774 to 802°C (1425 to 1475°F). |
| Application |
- Electrical connectors
- Current-carrying springs
- Welding electrodes
- Precision screw machined parts
|
- Current-carrying springs
- Precision screw machined parts
- Bearings
- Electrical/electronic connectors
|
- Electrical/electronic connectors
- Current-carrying springs
|
- Electrical/electronic connectors
- Corrosion resistant components
|
- Bearings
- Precision screw machined parts
- Current-carrying springs
|
CDA 172 Beryllium Copper Resists Corrosion, Radiation, and Heat
This alloy exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and is less prone to stress corrosion compared to other metals like brass or nickel silver. It performs better than copper-nickel or aluminum bronze in seawater environments, making it ideal for applications requiring both corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. A protective oxide layer forms on its surface during aging, acting as a barrier against environmental damage. This feature ensures good performance even at high temperatures.
C17200 Beryllium Copper Heat Treatment Process
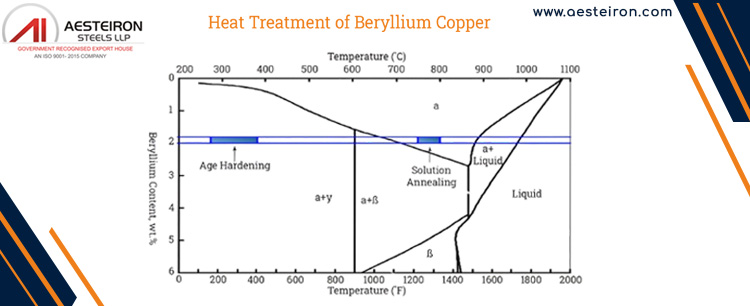
The heat treatment process involves two main stages:
| 1] Solution Annealing |
2] Age Precipitation |
- Prepares the alloy for age hardening by dissolving beryllium into the copper matrix to form a solid solution.
- Soaking Temperature: 750-800°C (1380-1470°F)
- Soaking Time: 30 minutes to 1 hour (depending on alloy composition and thickness)
- Cooling: Rapid quenching in water or oil
|
- Enhances strength and hardness by precipitating beryllium from the solution.
- Temperature: 300-400°C (570-750°F)
- Duration: 1 to 2 hours for high-strength applications
- Cooling: To room temperature
|
Understand the Chemical Composition and Mechanical Properties of BeCu Alloy
A thorough understanding of its chemical and mechanical properties will help you determine where and how this alloy can be best applied. The following table provides detailed information about its features, including high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, which make it suitable for demanding industrial and technological applications.
Beryllium Copper Alloys Composition
| Alloys Designation |
 |
High Conductivity |
High Strength |
| NGK Berylco |
B14 |
B8 |
B7 |
B25 |
B33/25 |
B165 |
| UNS |
C17510 |
C17510 |
C17530 |
C17200 |
C17300 |
C17000 |
| ISO/ EN Symbol |
CuNi2Be |
CuNi2Be |
CuNi2Be |
CuBe2 |
CuBe2Pb |
CuBe1.7 |
| ISO/ EN Number |
CW110C |
CW110C |
CW110C |
CW101C |
CW102C |
CW100C |
| Chemical Composition |
Beryllium (Be) |
0.2-0.6 |
0.2-0.6 |
0.2-0.4 |
1.8-2.0 |
1.8-2.0 |
1.6-1.8 |
| Cobalt (Co) |
– |
– |
– |
0.3 max |
0.3 max |
0.3 max |
| Nickel (Ni) |
1.8-2.5 |
1.4-2.2 |
 |
– |
– |
– |
| Ni+Co |
– |
– |
1.8-2.5 |
– |
– |
– |
| Co+Ni+Fe |
– |
–
 |
– |
0.6 max |
0.6 max |
0.6 max |
| Lead (Pb) |
– |
– |
– |
– |
0.2 min |
– |
| Al |
– |
– |
0.6 max |
– |
– |
– |
| Cu |
99.5 min |
99.5 min |
99.5 min |
99.5 min |
99.5 min |
99.5 min |
BeCu Mechanical Properties
| Â |
UNS C17200 |
UNS C17510 |
UNS C17000 |
UNS C17500 |
UNS C17300 |
| Hardness (Rockwell B) |
80.0 – 85.0 |
35 |
60 |
35 |
6 |
| Tensile strength |
1280 – 1480 MPa |
310 MPa |
483 MPa |
310 MPa |
469 MPa |
| Yield strength |
965 – 1205 MPa |
172 MPa |
32100 – 170000 psi |
172 MPa |
145000 – 175000 psi |
| Elongation |
15.0 – 30.0% |
28% |
45% |
28% |
48% |
C17510 BeCu Has a Conductivity Rating of 15-30%
While not as conductive as pure copper, C17510 offers excellent strength and hardness, making it highly sought after for applications that require both thermal and electrical conductivity. It is commonly used in high-performance electrical and mechanical systems.
Cryogenic Temperatures Properties of Berylco 25
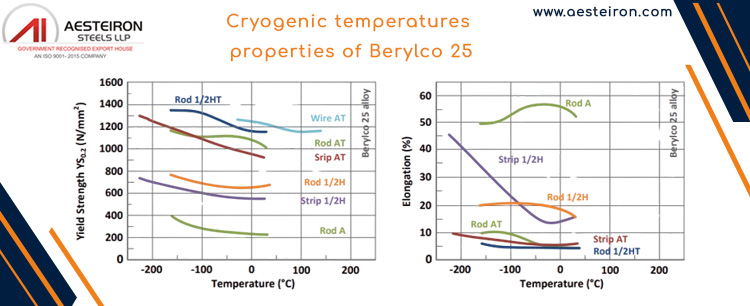
| Solution Annealed and Precipitation Hardened |
YS 0.2 (N/mm²) |
UTS (N/mm²) |
Young Modulus E (N/mm²) |
A% on 25mm (%) |
Charpy Impact (N/mm²) |
| Temperature in °C |
–100°C |
1080 |
1380 |
131000 |
8 |
6.9 |
| –200°C |
1170 |
1490 |
134000 |
9 |
9.6 |
| 20°C |
980 |
1340 |
123000 |
5 |
5.5 |
| –150°C |
1110 |
1400 |
131000 |
9 |
8.3 |
Beryllium Copper Alloys Physical Properties
| Physical Properties After Precipitation Hardening |
Specific Heat |
Melting Point |
Electrical Resistivity Ï (max) |
Coefficient of Linear Expansion |
Density |
Thermal Conductivity |
Modulus of Elasticity |
Fatigue Resistance |
Electrical Conductivity |
Magnetic Permeability |
Modulus of Rigidity |
Poisson’s Ratio |
| (Cal/(g.°C)) |
(°C) |
(10â¶Â·m) |
(x10â»â¶/°C) |
(g/cm³) |
(W/m.K) |
(N/mm²) |
(N/mm²) |
(%IACS) |
(μ=1+4) |
(N/mm²) |
| (Cal/(g.°C)) at 20°C |
 |
.m at 20°C |
at 20° to 200°C |
at 20°C |
at 20°C |
 |
at 10 cycles |
at 20°C |
(μ=1+4) |
 |
 |
| B165 |
0.1 |
890-1000 |
7.8 |
17.5 |
8.35 |
90-135 |
128 000 |
300 |
25 |
1.000042 |
49 000 |
0.3 |
B25
B33/25 |
0.1 |
865-980 |
7.9 |
17.3 |
8.26 |
84-130 |
130 000 |
300 |
25 |
1.000042 |
50 000 |
0.3 |
| B8 |
0.1 |
1005-1070 |
3.1 |
17.6 |
8.75 |
167-260 |
132 000 |
240 |
63 |
1.000031 |
52 000 |
0.3 |
| B14 |
0.1 |
1030-1070 |
3.8 |
18 |
8.75 |
167-260 |
132 000 |
240 |
50 |
1.000031 |
52 000 |
0.3 |
| B7 |
0.1 |
1050-1085 |
5.4 |
17.6 |
8.71 |
148-194 |
127 000 |
250 |
38 |
1.000027 |
49 000 |
0.3 |
Applications of Beryllium Copper in Telecommunications

| Telecommunication |
| Connectors and Contacts |
For reliable signal transmission and durability |
| Switches and Relays |
Excellent conductivity and wear resistance |
| Heat Sinks |
Manage heat in electronic devices |
| Shielding |
Offers efficient electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection |
| Spring Contacts |
Ensure longevity in circuit boards |
| Grounding |
Reduce electrical noise and improve safety |
| Terminals and Clips |
Provide secure electrical connections |
304 HRP Wire Rod
Jiangsu Manrui New Materials Co., Ltd , https://www.manruiwire.com




