Globally, electric vehicle (EV) sales have seen a significant rise in recent years. As a result, the need for charging infrastructure—both at home and in public spaces—has grown substantially. However, for many people, using an EV charger can still be confusing and unfamiliar. One of the most common questions new EV owners ask is how to pay for charging. This article aims to clarify that confusion by explaining the different payment options available and why there are so many ways to do it. While you can find free charging stations in some places—such as at your workplace or at certain businesses like supermarkets or restaurants—it's more likely that you'll need to pay for the majority of your charges. In fact, about 9 out of 10 times, you’ll be charged for public or even home charging depending on your electricity provider. The way you pay for EV charging varies depending on whether you're charging at home or in a public place. Let’s break it down into two main categories. Home charging is straightforward. Most home EV chargers are connected to your household electricity meter, so the cost of charging your car is simply added to your monthly utility bill. The price depends on your local electricity rate, and some providers offer off-peak rates that can help you save money if you charge during nighttime hours. Public charging is more complex and depends on the network or operator. Some stations require you to pay per use, while others offer membership plans with discounted rates. Payment methods often include apps, RFID cards, or contactless credit/debit cards. It’s important to understand which method works best for you based on your usage frequency and budget. Now let’s dive deeper into how paying for EV charging actually works. Unlike gas cars, where refueling is limited to gas stations, electric vehicles give you more flexibility in when and where you can charge. With electricity available almost everywhere, you have many options for charging your EV. But this variety also means that payment methods vary widely. Before diving into payment methods, it’s important to understand the different types of EV charging. Broadly, there are two kinds: private and public charging. Private charging, also known as home or residential charging, refers to charging at your own residence or in a private parking area. These are typically the most convenient and cost-effective options. Public charging, on the other hand, is available in locations such as supermarkets, malls, hotels, and gas stations. These are accessible to everyone but may require registration or a subscription to certain networks. The way you pay depends on whether you’re using a private or public charger. Let’s take a closer look at each. Paying for home charging is simple. Since these chargers are connected to your home’s electrical system, the energy used is tracked and added to your electricity bill. The cost varies based on your electricity provider, the power of your charger, and your driving habits. Home charging is usually the most cost-effective option, especially if you take advantage of lower off-peak rates. Some utility companies even offer special EV-friendly plans to help reduce your costs. Public charging stations come in various forms and prices. While some allow you to pay directly at the station, many require you to sign up for a service or use an app. Payment methods include subscriptions, RFID cards, and contactless card payments. It’s worth noting that the cost of public charging can vary significantly depending on the speed of the charger and the network you're using. Fast chargers, for example, tend to be more expensive than slower ones. One of the biggest challenges with public charging is identifying the user. Each network has its own authentication process, which can make the experience confusing for first-time users. Let’s explore the different methods and how they work. There are currently three main ways to authenticate yourself at a public charging station. A new method called “plug and charge†is also being developed to simplify the process. For most methods except contactless card payments, you can choose between a subscription or a pay-as-you-go plan. Subscriptions often offer cheaper rates, while pay-as-you-go gives more flexibility. Many public charging stations now support payment through dedicated apps. These apps let you connect, authenticate, and pay for your charging session. You can either subscribe to a plan with discounted rates or pay per use. Some public charging stations accept RFID cards or key fobs issued by the operator. These devices store your account information, allowing you to access the station without a smartphone. Like apps, you can choose between a subscription or pay-per-use model. Some public stations allow you to pay using a contactless credit or debit card. This is the simplest method, but it can also be the most expensive in the long run since it doesn’t offer discounts or memberships. Despite the variety of payment methods, the current system can be confusing and inconsistent. Fortunately, new standards and technologies are emerging to simplify the process. One such development is “Plug and Charge,†an international standard designed to streamline the charging process by automatically identifying the user when the car is plugged in. Known officially as “Road Vehicles – Vehicle to Grid Communication Interface,†Plug and Charge is an ISO standard (ISO 15118) that aims to eliminate the need for manual authentication at public charging stations. Instead, your vehicle will automatically communicate with the charger, making the process seamless and secure. As EV adoption grows, governments are stepping in to create more standardized and fair charging systems. For example, the US is developing the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) program, while the EU is working on Fit for 55 and the Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation (AFIR). Roaming allows EV drivers to charge at stations across different countries without needing multiple accounts or subscriptions. Similar to mobile roaming, it enables seamless charging experiences regardless of location. Paying for EV charging can be complicated, especially for new drivers. However, as technology advances and regulations evolve, the future looks promising for a more unified and user-friendly charging experience. To learn more about EV charging regulations in Europe, check out our dedicated blog. If you want to know more about using public charging stations, read our article on public EV charging. Shenzhen New Gaopin Sports Goods Co,Ltd , https://www.newgaopin.comDo You Have to Pay to Charge an Electric Car?
How to Pay for Electric Car Charging: A Quick Overview
Charging at Home
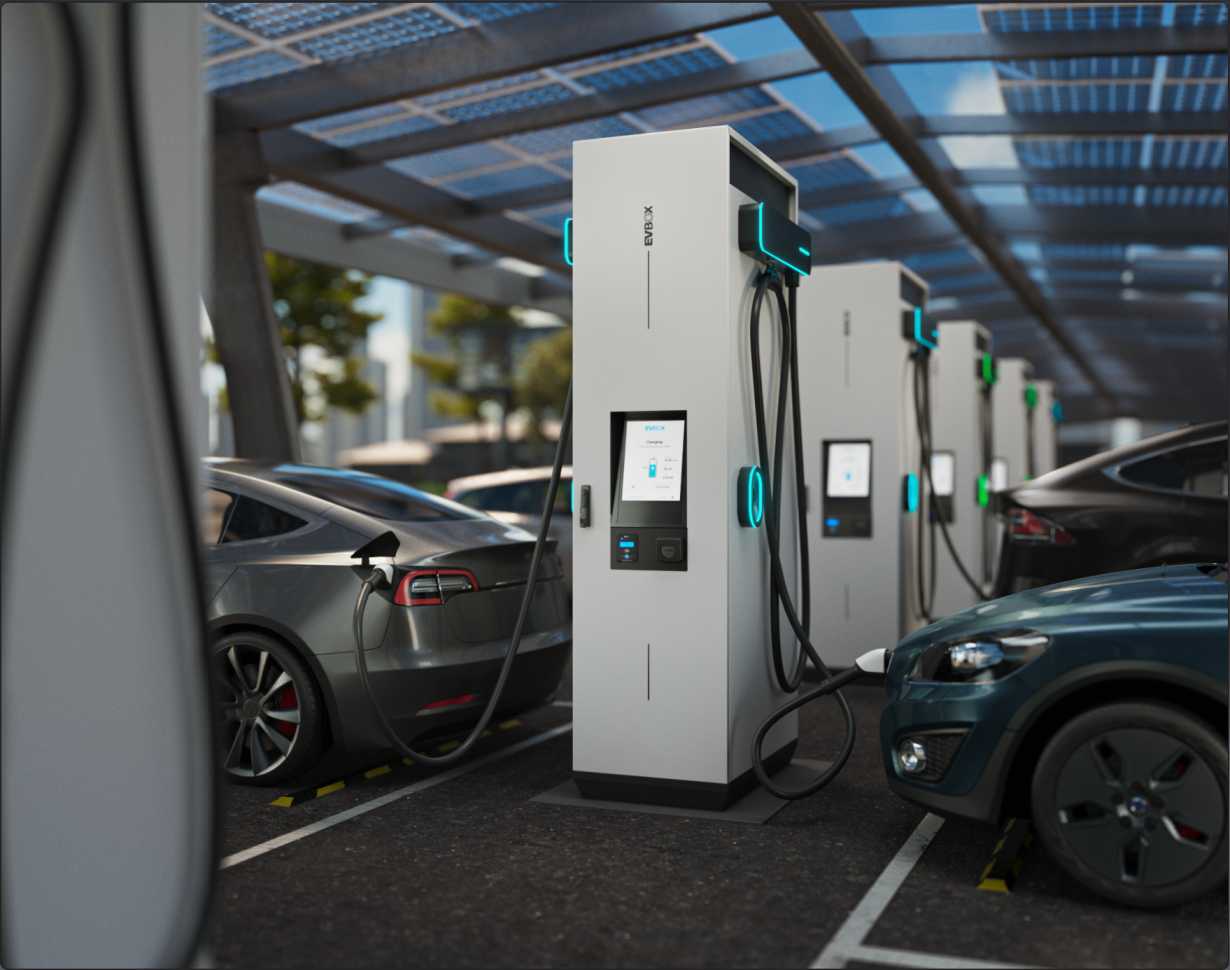
Charging in Public
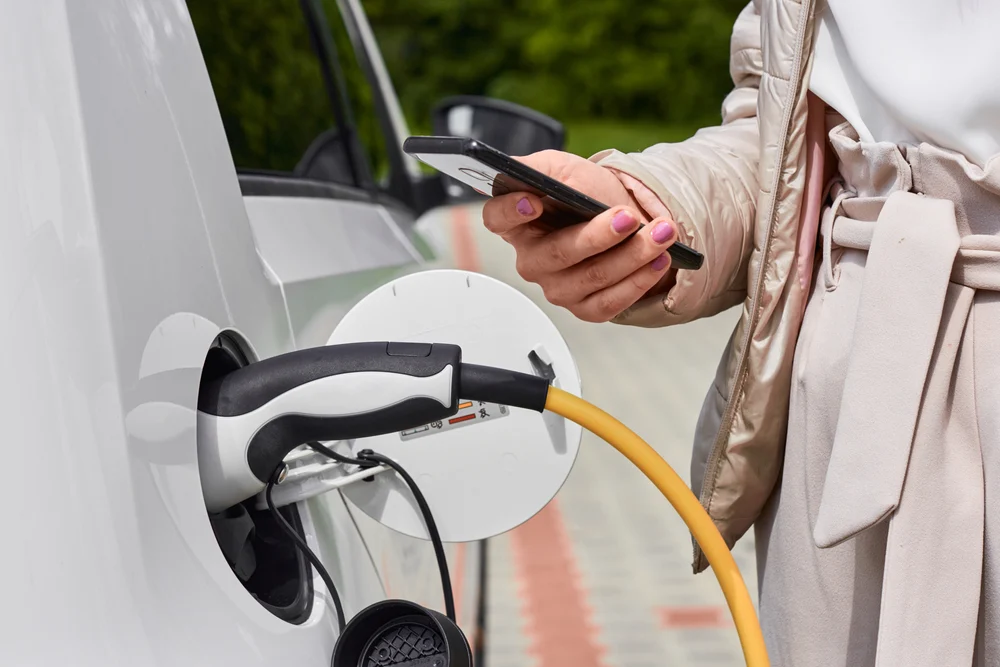

How Do You Pay for Electric Car Charging?
Different Types of Charging
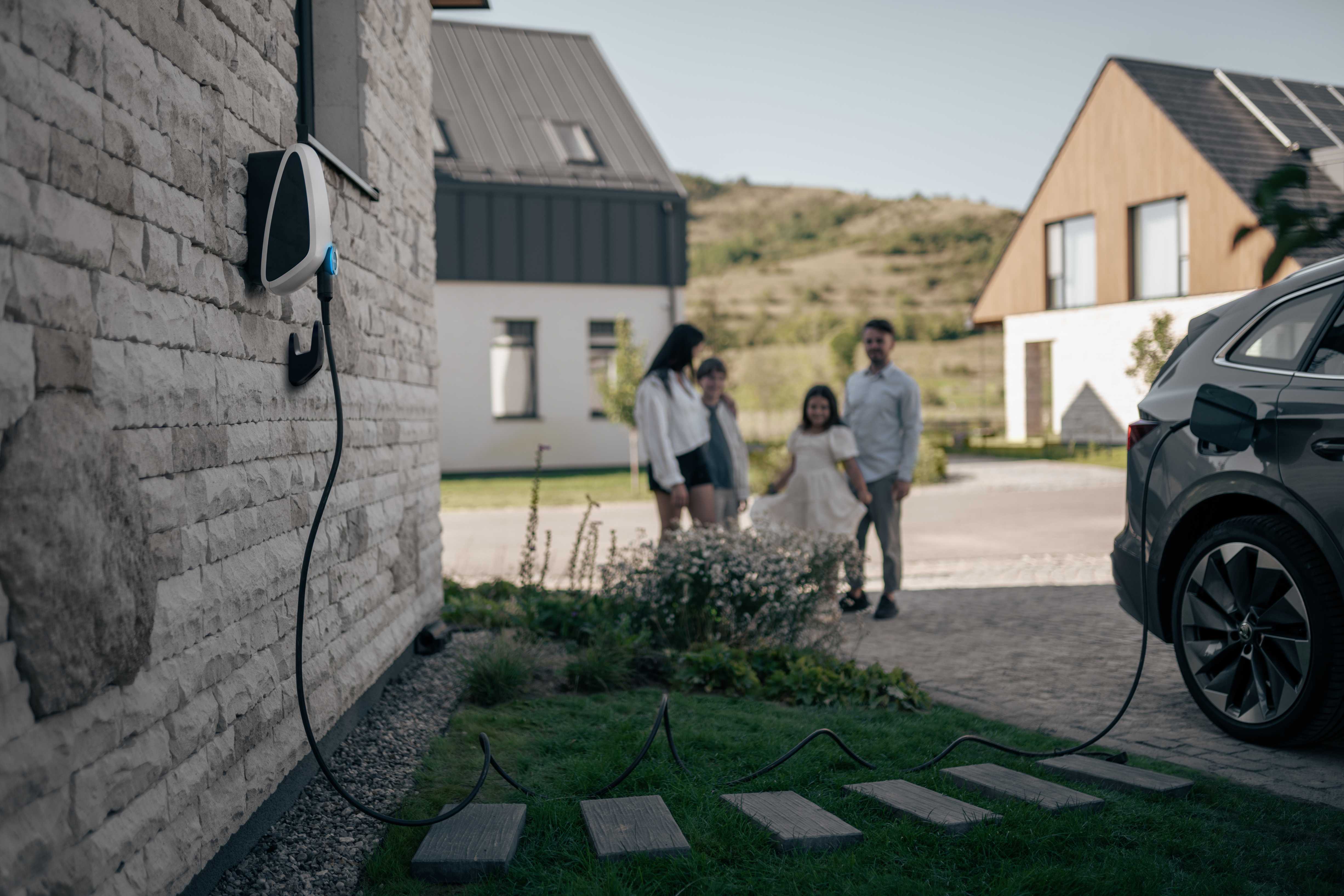


How to Pay for Home Charging
How to Pay for Public Charging
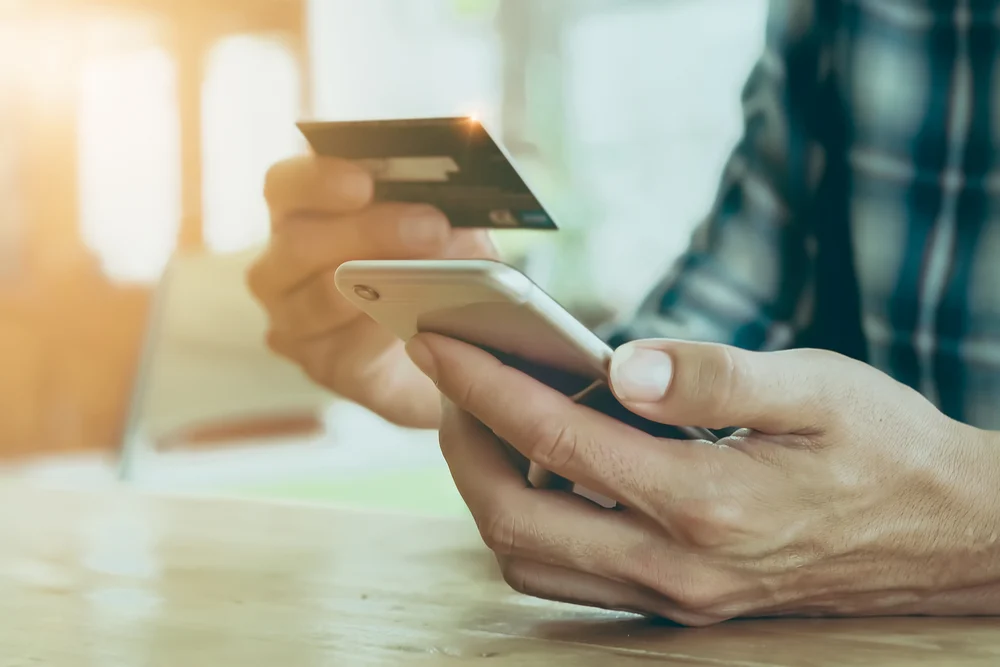

How You Pay Is Connected to How You Identify Yourself
Charging via an App

RFID Card / Key Fob

Contactless Payment
What’s Coming Next for Public Charging Payments?
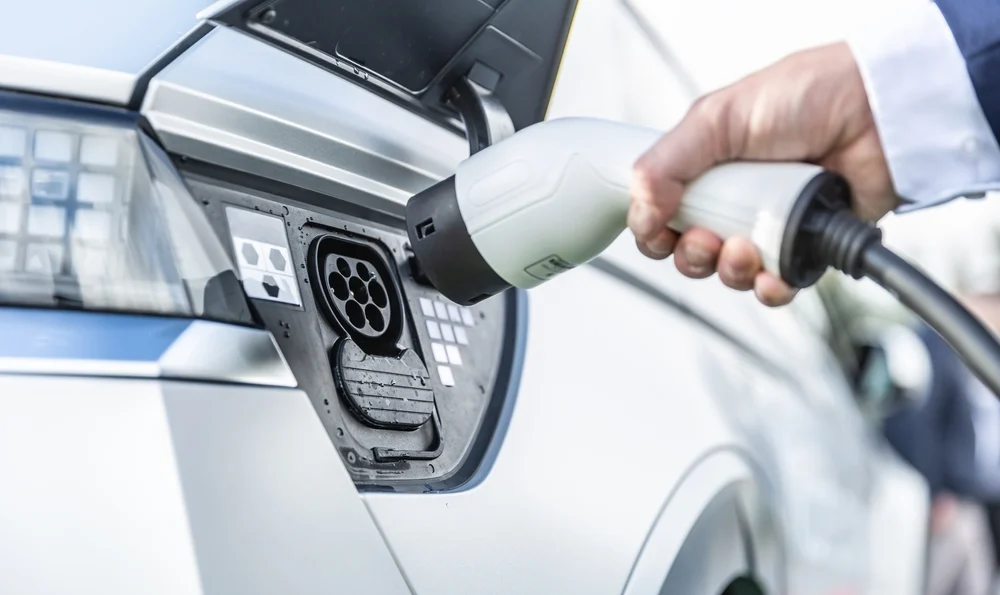

Plug and Charge
Government Regulations and Consumer Protection
EV Roaming
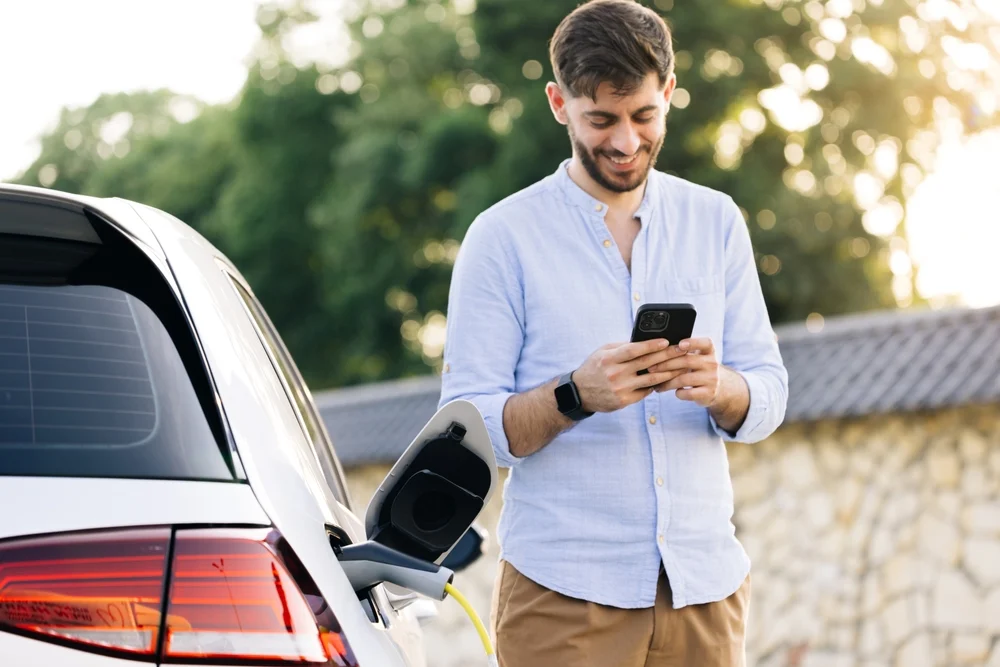

How do you pay to charge an electric car?
Globally, electric vehicle (EV) sales have seen a significant rise in recent years. As a result, the need for charging infrastructure—both at home and in public spaces—has grown substantially. However, for many people, using an EV charger can still be confusing and unfamiliar. Shenzhen New Gaopin Sports Goods Co,Ltd , https://www.newgaopin.com